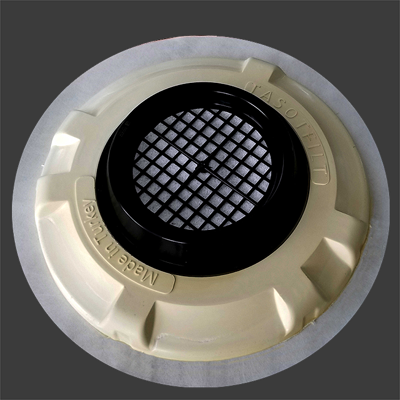
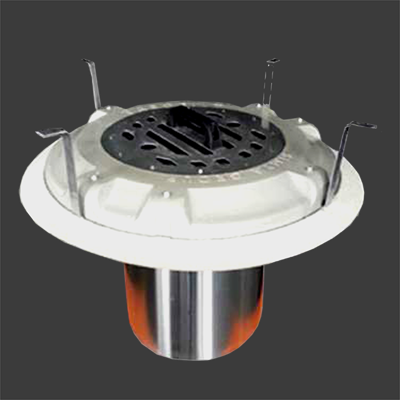
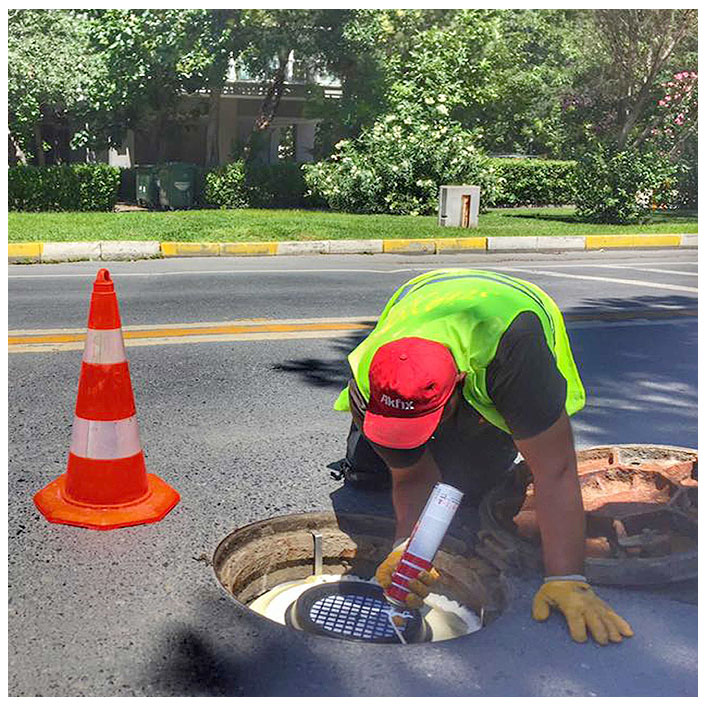
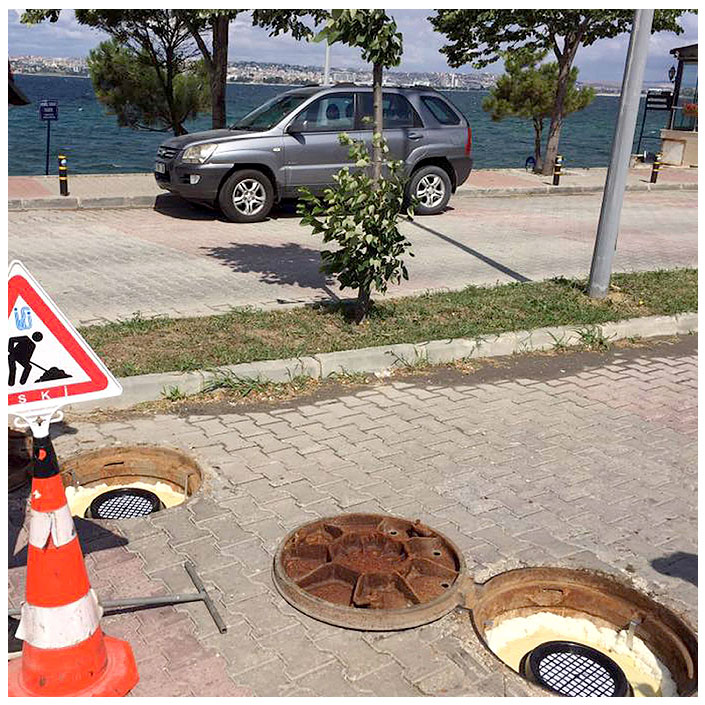
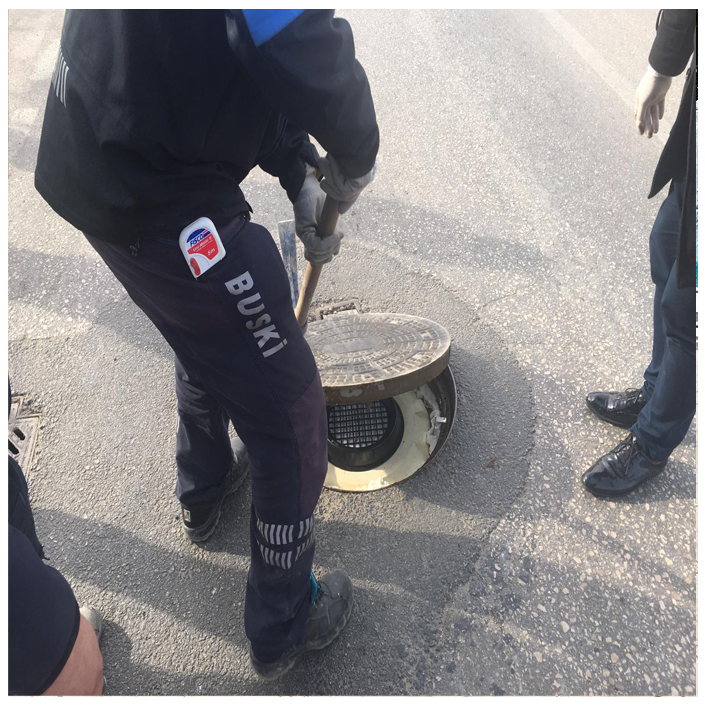
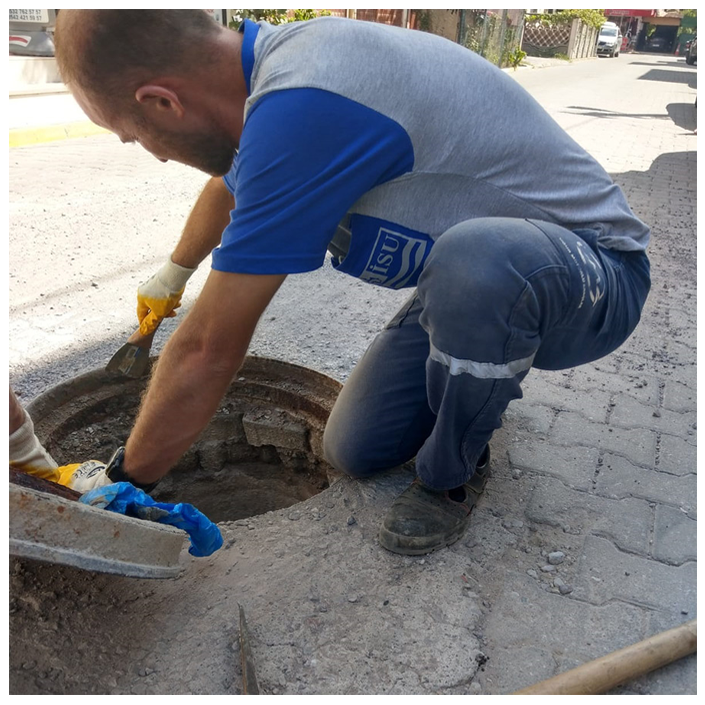
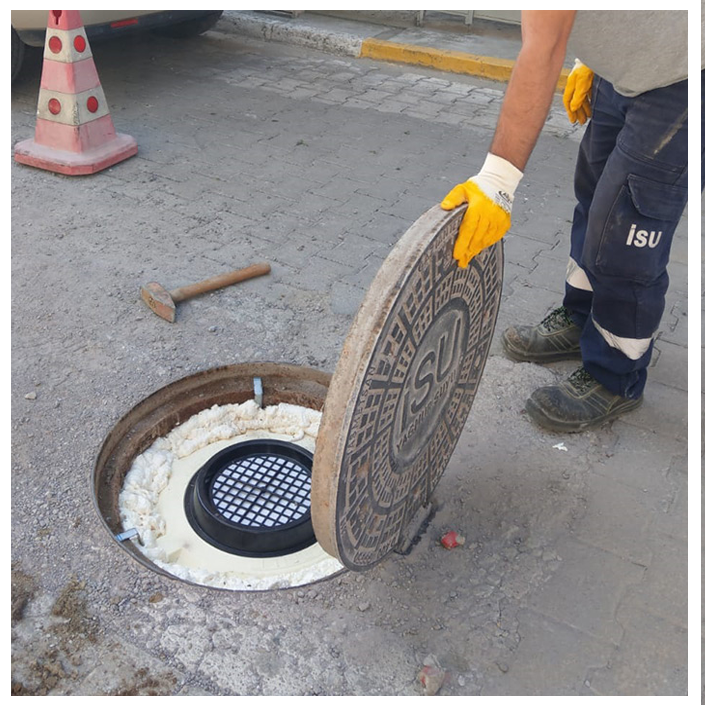
Tasotfilt is designed to ensure that gases follow the longest possible path within a minimal volume, maximizing their contact with the filtration media. It does not obstruct the passage of gas or water, allowing up to 35m³/min of gas flow through the wastewater line without causing pressure buildup.
The Role of Oxygen in Wastewater Systems
A major issue in wastewater pipelines is the drop in oxygen levels. When biodegradable materials in wastewater decompose rapidly due to bacterial activity, oxygen levels decrease, creating an anaerobic environment. If air is introduced into the system via fans, the pressurized air escapes through the nearest manhole covers, preventing fresh air from circulating within the pipeline.
Tasotfilt regulates the controlled release of pressurized air from manholes, ensuring that fresh air moves through the wastewater line. This promotes an aerobic environment throughout the pipeline, preventing unwanted conditions and ensuring system stability.
Wastewater systems do not operate uniformly throughout the day. At night, reduced water usage slows the system, leading to a rapid drop in oxygen levels and the onset of anaerobic conditions. When water flow increases in the morning, oxygen re-enters the system, but harmful gases formed overnight—along with decreased pH levels—can damage the structural components of the wastewater system. During low-flow periods, additional air supply is necessary, making Tasotfilt crucial for system balance.
Filtration Mechanism
The filter cartridge consists of interwoven labyrinths that guide gases in a helical motion toward the center.
• As gases pass through the filter, they come into contact with the media, breaking hydrogen bonds and separating molecules.
• The media chemically binds harmful gases through Van der Waals forces.
• Certain bacteria, such as Sulfobacter oxydans, present on the media surface, become active and break down gases.
• A dry chemical section in the center neutralizes harmful organisms in the gas, releasing clean air into the atmosphere.
• Rainwater entering the filter disrupts the Van der Waals bonds, allowing the gases to form new hydrogen bonds with water molecules. These are then washed into the wastewater system, reaching treatment facilities. This process regenerates and renews the filter.
Durability and Materials
All materials used in the filter assembly are selected to withstand pH levels as low as 2.
• Mounting brackets are made of stainless steel.
• The housing is rigid polyurethane (PU).
• The cartridge is made of recyclable polyethylene (PE).
Only the cartridge is replaced during maintenance, while all other components remain fixed.
Safety Features
• The filter is buoyant and will not sink if it falls into wastewater.
• A safety ring prevents loss if the filter becomes dislodged.
• The safety ring, made of stainless steel cable, typically secures the filter to the manhole cover hinge, ensuring stability.
Future Advancements
In the next stage, bacteria from treatment plants could be introduced into wastewater pipelines. This innovation would enhance the wastewater ecosystem, leading to significant environmental benefits. It could reduce energy consumption in treatment plants, eliminate sludge problems, and create a closed-loop system.